
STA1005 - Quantitative Research Methods
Lecture 3: Collect, Clean, and Transform Data
Always Prepare the Data
To efficiently perform any kind of analysis on data, it is essential to format the data file in the most suitable way.
To do so, 3 steps are required:
- Understanding how data have been collected
- Cleaning the data from any noise
- Transforming the data in order to obtain the relevant variables
1. Collecting Data
Data Everywhere

What are Big Data?
- In general Spreadsheet that are too large or too complex to be handled by conventional tools
- For me Spreadsheet that are larger then Microsoft Excel’s Limits (2016)
- Total number of rows: 1,048,576 rows
- Total number columns: 16,384 columns
Collecting Data
A tool is required to collect data, but there are tools to measure anything:
- Naturalistic Objects
- Economic Status
- Social Events
- Psychological States
- …
Focus on Psychometric Scales
A psychometric scale is a series of questions (items) used to measure a latent variable
A score has to be calculated from all the items to produce the variable to analyse:
- Average of all items (equal contribution to the latent variable score)
- Factor analysis (unequal contribution to the latent variable score)
Focus on Psychometric Scales
A scale should have been validated by its authors:
- Don’t change the items except when possible
- Don’t change items’ range of possibilities
To be analysed, a scale has some requirements:
- All the items must have the same range of possibilities/modalities
- All the items must be analysed in the same direction
- All the items must correlate together (scale reliability)
- A unique theoretical construct score has to be calculated from all the items
Focus on Psychometric Scales
Online Survey Software are replacing the paper-pencil method. Here is a list of some:
- Google Form (from your google drive, DCU hosted)
- Qualtrics (https://dcusurveys.qualtrics.com/ DCU account)
- Survey Monkey (https://www.surveymonkey.com/, NOT FREE)
- LimeSurvey (https://www.limesurvey.org/, NOT FREE)
- Zoho (https://www.zoho.com, NOT FREE)
- Gorilla Experiment (https://gorilla.sc, NOT FREE)
Focus on Psychometric Scales
Warning
- Always ask for age and gender in a survey
- Participant recruitment by list of contact/email has between 15% and 10% of answer rate
Platforms to find and reward participants:
- Amazon MTurk (https://www.mturk.com/ mainly US and India)
- Prolific Academic (https://www.prolific.co/ world wide)
- Qualtrics (https://www.qualtrics.com/uk/research-services/online-sample/)
- Survey Monkey (https://www.surveymonkey.com/mp/find-survey-participants/)
Latent Variables
Scale to measure the “Perceived Ease-of-use” of MS EXCEL in 4 items were measured from 1 “totally disagree” to 7 “totally agree”:
- q1. I think learning MS EXCEL is easy
- q2. Understanding MS EXCEL is easy
- q3. I am good at using MS EXCEL
- q4. I think using MS EXCEL is easy
Latent Variables
Here are the results with 3 students. The score of the “Perceived Ease-of-use of MS EXCEL” latent variable is calculated using the average of all items.
| employee | q1 | q2 | q3 | q4 | peo_score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sinead | 7 | 5 | 7 | 7 | 6.50 |
| Patrick | 5 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 5.25 |
| Damien | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2.25 |
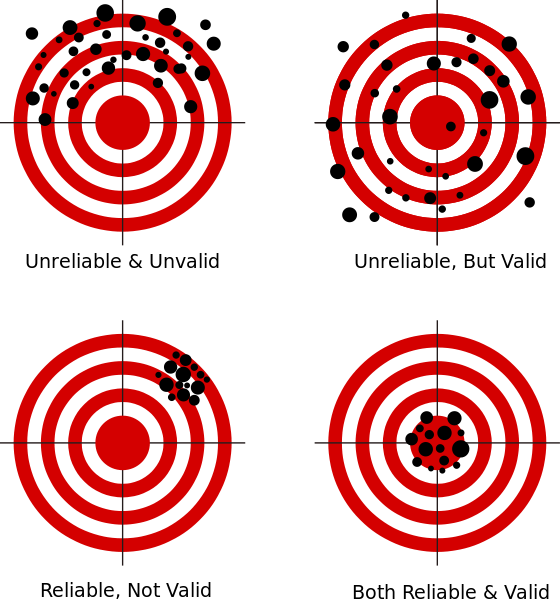
Validity and Reliability
Validity = is my variable measuring the construct that I think I am measuring?
- Does the measurement make sense?
- Would the results be reproduced with another scale measuring the same latent variable?
- Are the results correlated to latent variables that are related?
Validity test is only performed when a scale is created (no need for existing scales)
Validity and Reliability
Reliability = consistency of items inside a measurement
- Test-retest reliability
- Inter-rater reliability
- Correlation inter-item (Cronbach’s alpha)
Reliability test is performed every time a scale is used but only using Cronbach’s alpha
Validity and Reliability

Survey Example
Perceived Usefulness:
- (PU1) Using MS EXCEL would improve my performance in statistical analysis
- (PU2) Using MS EXCEL would increase my productivity in statistical analysis
- (PU3) Using MS EXCEL would enhance my effectiveness in statistical analysis
- (PU4) Using MS EXCELR would make it easier for me to engage in statistical analysis
- (PU5) I think using MS EXCEL is very useful for me to engage in statistical analysis
Perceived Ease-Of-Use:
- (PEOU1) I think learning to use MS EXCEL is easy
- (PEOU2) I think doing what I want via MS EXCEL is easy
- (PEOU3) I think becoming skilful at using MS EXCEL is easy
- (PEOU4) I think using MS EXCEL is easy
Behavioural Intention:
- (BI1) Assuming I had access to MS EXCEL, I intend to use it
- (BI2) Given that I had access to MS EXCEL, I predict that I would use it
Survey Example
Accessing your Data
From a Google Form
- Login Google Account (be sure to use the DCU account)
- Go to Drive
- Click on your Survey form
- Click on Response
- Download Response Spreadsheet as .csv
From a Qualtrics survey
- Login Qualtrics (DCU login/pwd) https://dcusurveys.qualtrics.com/
- Click on Data & Analysis
- Click on Export & Import > Export Data…> CSV (Use numeric values)
Warning
- Always save the unmodified raw version of your data on the cloud (e.g., google drive, dropbox, one drive, …)
- Make sure you can download them as a .csv file.
2. Cleaning Data
An Essential Step
Cleaning Data means removing any non-essential feature included in the spreadsheet
If you don’t have big data… then use Microsoft Excel!
If you do have big data, then use R or Python.
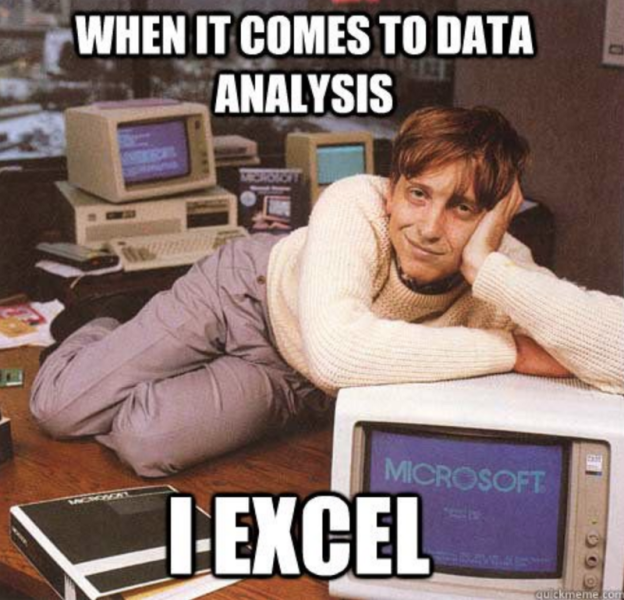
Question from Kareem
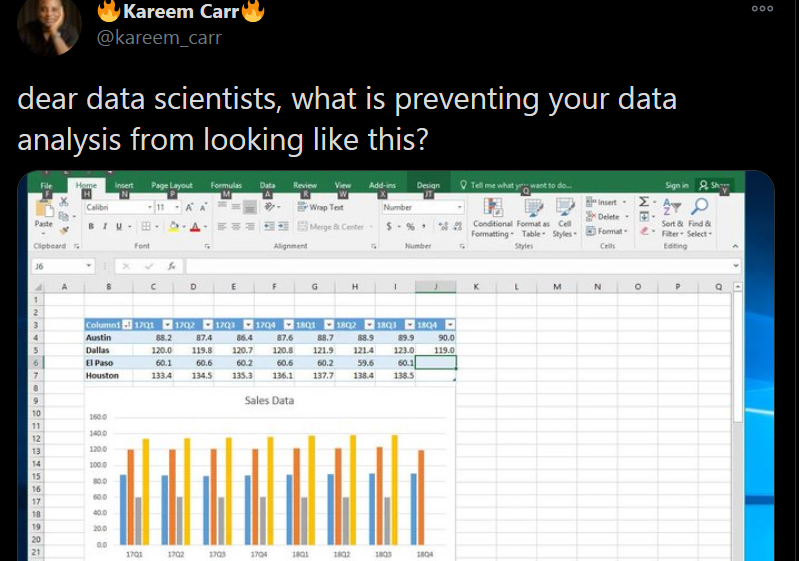
️ Your Turn!
Find what is going wrong with this table
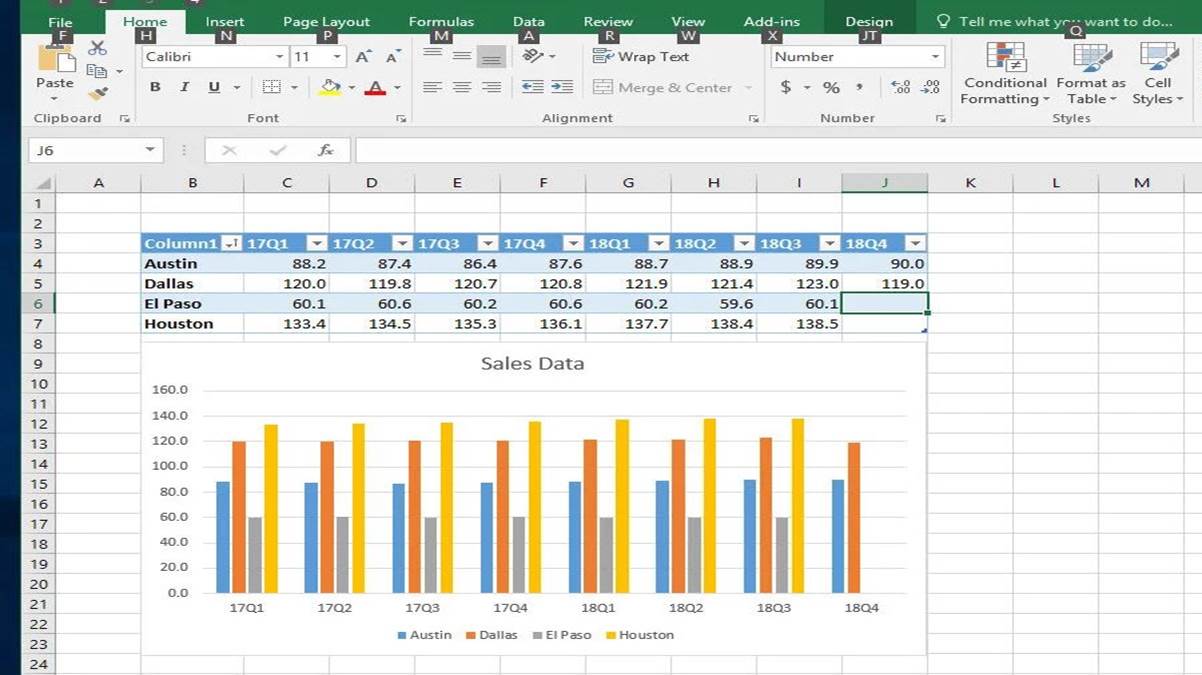
Answer from Michael
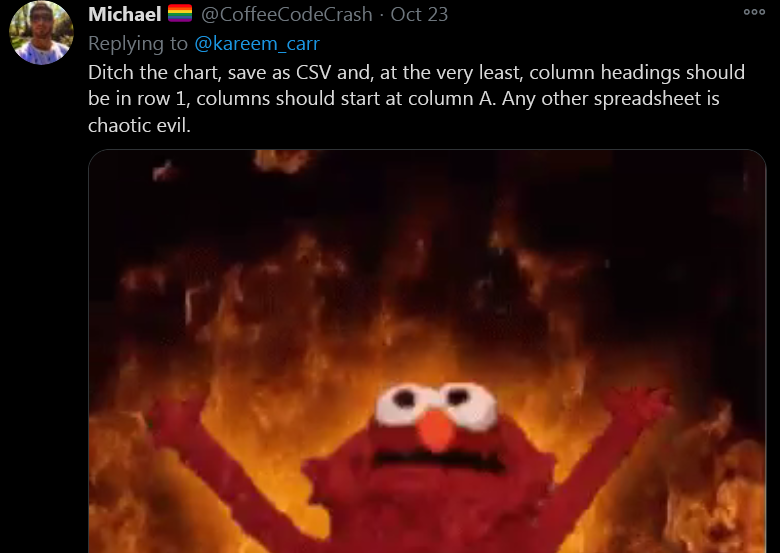
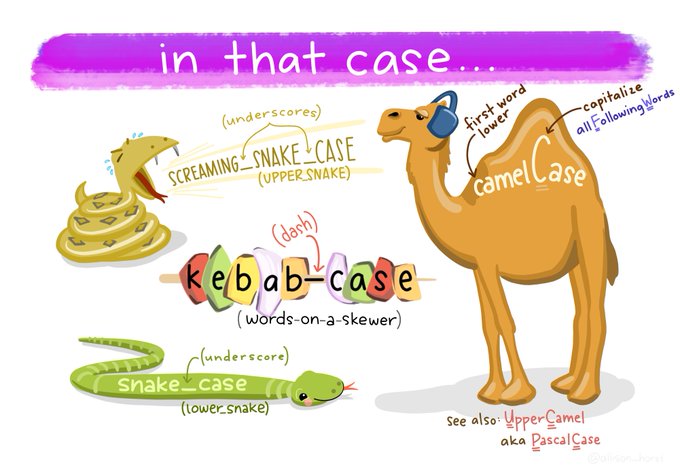
Use a Name Convention
An addition to Michael’s list would be to transform headers with a proper naming convention
My suggestion is snake_case: all small letter and words separated by “_”
To Clean Data …
1. Ditch the chart and all non values
Charts can mess up with other software
2. Column headings in row 1
No more than 1 heading row and remove blanks
3. Columns start at column A
Remove blanks before data
4. Use a naming convention
snake_case is preferable but any would do
5. Save as .csv file
Better format and keeps only the current sheet
️ Your Turn!
On the module Loop page, got to “Lecture Data” and download the document called “unicef.xlsx”
Open and clean the 1st sheet of this file but only until column P, remove all other columns
15:00
3. Transform Data
Master the Key Transformations
- Extension
- Reduction
- Direction
- Aggregation
- Combination
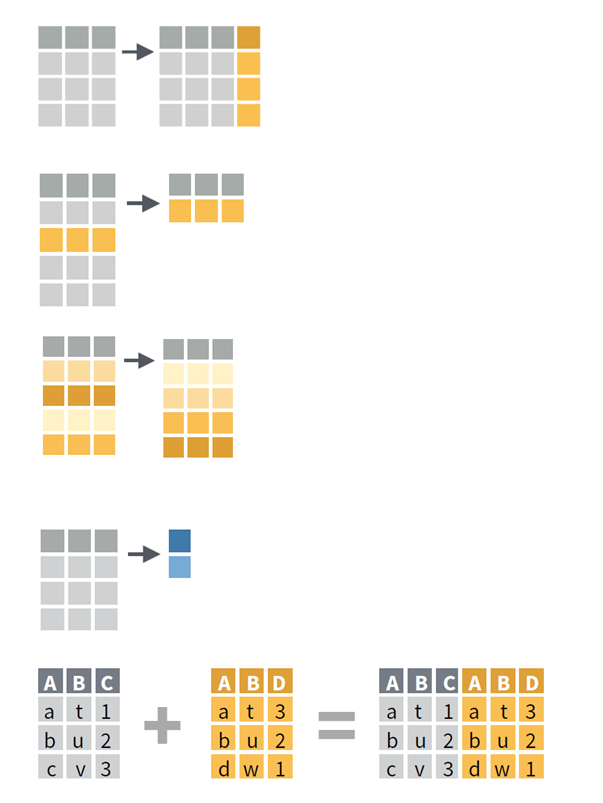
Extension
Extension = Create a new column
In MS Excel:
- First row is row name (name convention)
- Second row is the function (starts with = sign)
- Following rows are applying the function (double click bottom right corner of the cell)
Excel Functions
For numeric values
- Numeric operator ( + - / *)
- $ (freeze row and/or column)
- COUNT(), MIN(), MAX(), SUM(), AVERAGE (), STDEV()
For character strings
- LEFT()
- CONCAT()
Extra function
- IF(condition, value if true, value if false)
- IFS(condition 1, value if 1 true, condition 2, value if 2 true, …)
Reduction
Reduction = Keep only certain values
In MS Excel:
- Select header row
- In Data tab, use Filter
- Click the drop-down arrow for the column you want to filter
- Choose values to filter
Excel Filters
Warning
- Rows already filtered have a row index are coloured in blue
- Copy-Paste filtered table in a new document if you want to work only on these values
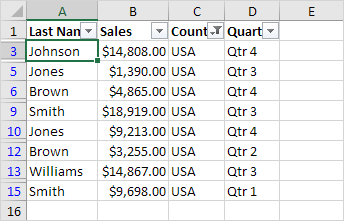
Example of data filtered buy the column Country to keep only values corresponding to USA
Direction
Direction = Arrange Row Order
In MS Excel:
- Select table
- In Data tab, use Sort
- Choose column to sort and how to sort
Warning
- Be careful of taking into account all the table (all rows & all columns)
- Double check if all columns changed!
Aggregation
Aggregation = Summary of Column
In MS Excel:
- Simple = use function at the end of a table
- Complex = use pivot table
Pivot Table in Excel
- Select data
- In Insert, use Pivot Table
- Drag columns to sort by row/column
- Choose value column to be aggregated
- Choose type of aggregation
If you want to use the Pivot Table for further analysis:
- Copy-Paste it in another document
- Paste as value (removes dynamic link)
Combination
Combination = Join two tables
In MS Excel:
- One Column = vlookup function
- Multiple Columns = Power Query (Windows only)
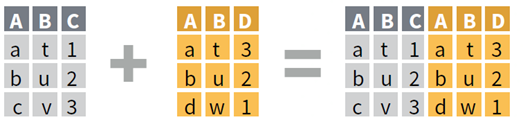
=VLOOKUP(value, table, col_index, [range_lookup])
- value: Value to look for in the first column of a table
- table: Table from which to retrieve a value
- col_index: Column in the table from which to retrieve a value
- range_lookup: TRUE = approximate vs. FALSE = exact match
Demonstration
️ Your Turn!
On the module Loop page, got to “Lecture Data” and download the document called “organisation_alpha.xls”
- Extension: Create a new variable/column which is the average response to all the questions from the survey for each employee (q1 to q9)
- Reduction: Filter employee’s 2019 salary to keep only employees with a salary higher than 30k
- Aggregation: Calculate the average salary by gender and by location
- Combination: Using the VLOOKUP function, add to the table a column corresponding to the 2017 salary located in the 2nd sheet
15:00
Extra Analytic Tips
Tidy Data
- Each variable has its own column
- Each observation is placed in its own row
- Each value is placed in its own cell
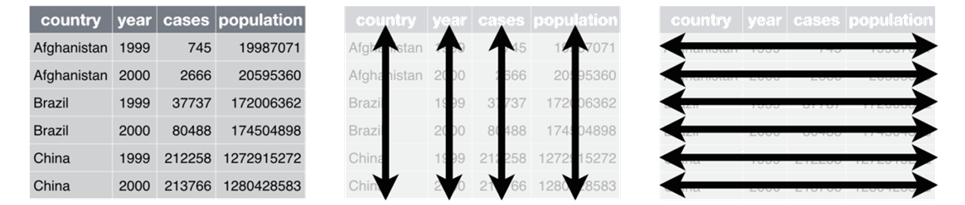
Long or Wide?
Long Format
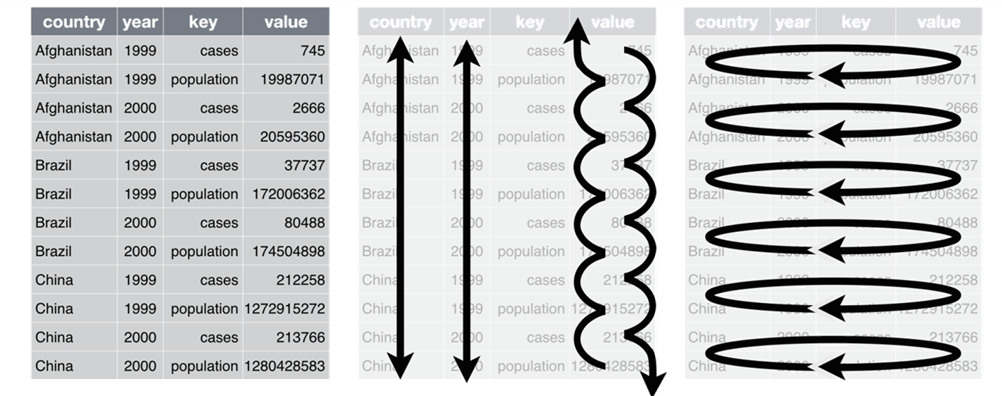
Long or Wide?
Wide Format
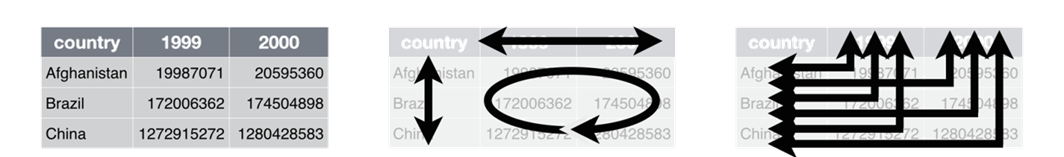
Long or Wide?
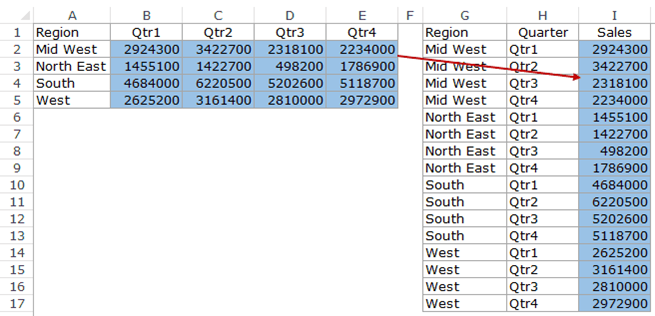
Reshape Table in Excel
In Data tab:
- Get Data/New Query> From File > From [Workbook/CSV]
- Select your file > Edit
- Select columns to be reshaped
- Transform
- Pivot Columns: from long table to wide table
- Unpivot Columns: from wide to long table
Demonstration
Repeat Action Automatically
In Excel, the Macro button allows to record a sequence of actions and to reproduce these actions:
- VBA Code automatically recorded
- Useful to process similar data files
Recording a Macro:
- View Tab
- Use Macros > Record Macro
- Do your actions
- Save the macro with a keyboard shortcut
- Use the macro again to reproduce your actions
️ Your Turn!
Researchers are measuring how good at chess are LLM Algorithms (ChatGPT, Gemini, …), they want to test the following hypotheses:
H1: The average number of move to win at a chess game is different for at least 1 of the LLM Algorithms
Reshape the datafile “chess_llm.csv” to have 1 predictor variable called “llm_algorithm” and 1 outcome variable called n_moves_to_win”
10:00
Thanks for your attention
and don’t hesitate to ask if you have any questions!
