02:00
Lecture 3: Publishing with GitHub Pages
BAA1028 - Workflow & Data Management
For Today
Requirements
1. Find these slides at:
https://damien-dupre.github.io/BAA1028/lecture_3
2. Homework Exercise done
Objectives
1. Host your ePortfolio on GitHub
2. Publish your ePortfolio with GitHub pages
Any questions?
Then, it’s time to enter …

Host your Website on GitHub
GitHub
GitHub has a lot of different functions. For now, we will only see how to use it to published the html document output from our notebook file.

What is GitHub
Primary used to collaborate on code development, it became multi-purpose:
- Version Control
- File and Code Storage
- Collaboration Projects
- Social Media for Developers
- Online Publication & Website Host
- Automatic Actions
And even more that I am not aware of!
What is GitHub
Primary used to collaborate on code development, it became multi-purpose:
- Version Control
- File and Code Storage
- Collaboration
- Developers Social Media
- Online Publication & Website Host
- Automatic Actions
And even more that I am not aware of!
Your Turn: Sign In or Sign Up
- Go to https://github.com,
- Click Sign In or Sign Up (if you have already done it),
- If you are creating an account, fill all requested information.
Important
Your user name will become extremely important in your future (i.e., working with data teams, visibility of employers), firstname-name is usually good.
Welcome to GitHub

How does GitHub Work?
The core principle of GitHub is a remote desktop (or profile) with a folder called Repository for each project you are working on or you worked on (also called “Repo” if you want to use the slang).

Your First Repository
Your First Repository
Follow the steps here after to create a Repository:
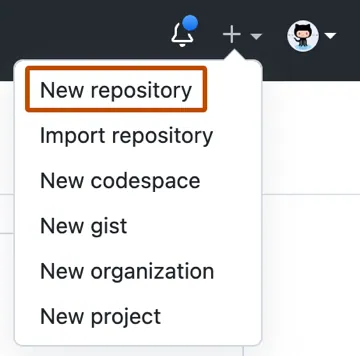
- In the upper-right corner of any page, use the
+drop-down menu, and select New repository.
Your First Repository
Your First Repository
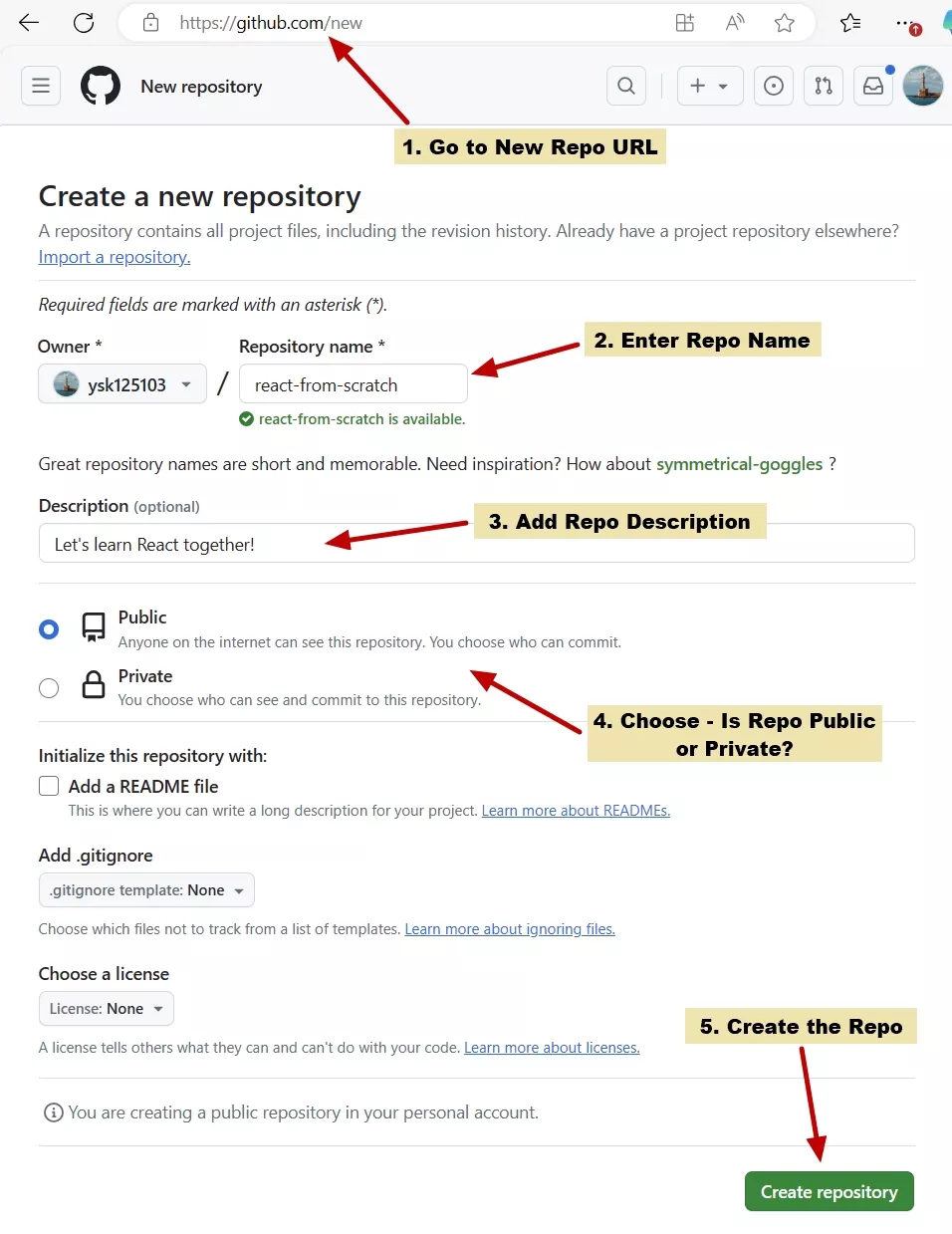
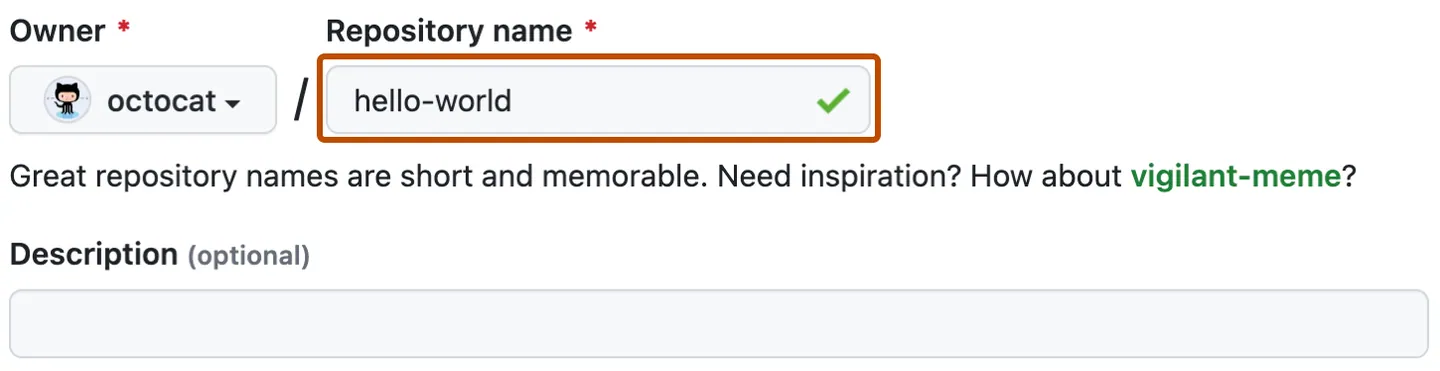
- Type a short, memorable name for your repository, like
hello-world.
Important
In the future, these test repositories should be removed to have a clean account.
- Optionally, add a description of your repository. For example,
My first repository on GitHub.
Your First Repository
Choose a PUBLIC repository visibility. For more information, see about repositories,
Tick ✅ Add a README file,
Click Create repository.
Congratulations! You’ve successfully created your first repository, and initialized it with a README file.

Always Commit Changes
In GitHub, a commit is a saved change to a project’s source code or other files. When you make changes to a file in a GitHub repository, you create a new version of that file.
A commit contains a snapshot of the changes you’ve made to one or more files, along with a message that describes the changes. This message should be descriptive and clear, so that other developers can understand what changes you’ve made and why.
Important
Everytime you want to make a change in your repository, you need to commit these changes.
Your First Commit
Your First Commit
When you created your new repository, you initialized it with a README file. README files are a great place to describe your project in more detail, or add some documentation such as how to install or use your project. The contents of your README file are automatically shown on the front page of your repository.
Follow the steps here after to commit a change to the README file.
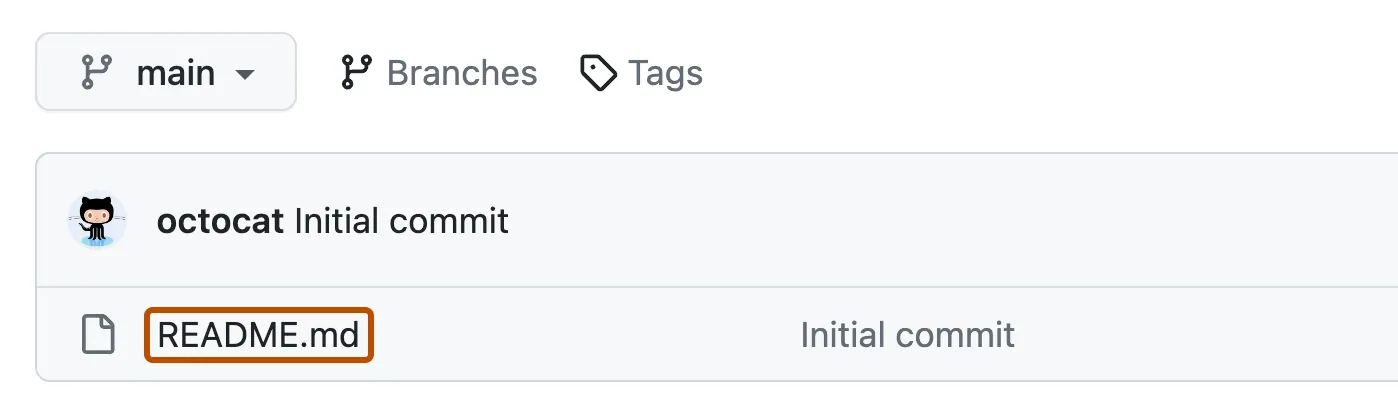
- In your repository’s list of files, click README.md.
Your First Commit
- In the upper right corner of the file view, click on the pen icon to open the file editor ✏️,

- In the text box, type some information about the project.
Your First Commit
- Above the new content, click Preview to review the changes you made to the file.
- Click Commit changes….
Your First Commit
- In the “Commit message” field, type a short, meaningful commit message that describes the change you made to the file.
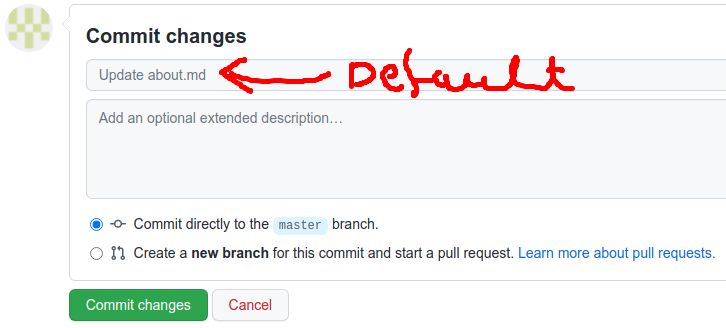
Below the commit message fields, decide whether to add your commit to the current branch or to a new branch. Select commit directly to the
mainbranch for now.Click Commit changes.
Important
For collaborative projects never commit to the main branch
GitHub Pages
GitHub Pages is a web hosting service offered by GitHub that allows you to host static websites directly from a GitHub repository. This means you can use GitHub to store and version control your website’s code, and then host it for free using GitHub Pages.
Your website will then be published at a URL based on your GitHub username and repository name (e.g., username.github.io/repository).

Your Turn: Turn on GitHub Page
Turn on GitHub Pages for your project repository:
Go to Settings and find Pages on the left pane,
In Branch, instead of None select Main and click Save,
Click on Actions and wait that “pages build and deployment” finishes,
When it’s done, go to https://username.github.io/repositoryname.
03:00
Your Turn: Add New Files to your Repository
Important
For this exercise, you need the index.html file from the website template that you have downloaded and modified last time.
In your Repository Page in GitHub, Click Add files then on Upload files,
Drop or choose all the file
index.htmlIn the main box and commit your changes and observe the changes on your website.
02:00
Your Turn: Add New Files to your Repository
In your Repository Page in GitHub, Click Add files then on Upload files,
Drop or choose all the subfolder and files contained in the local website folder beside
index.html,In the main box and commit your changes and observe the changes on your website.
02:00

Thanks for your attention and don’t hesitate to ask if you have any questions!
@damien_dupre
@damien-dupre
https://damien-dupre.github.io
damien.dupre@dcu.ie